Soil Analysis & Mapping
Overview
Soil analysis and mapping is a precision agriculture process that evaluates the physical, chemical, and biological properties of soil to understand its fertility, nutrient status, moisture levels, and overall productivity potential. Using sensors, laboratory tests, drones, and GIS tools, the system generates spatial soil maps showing variations across the field, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions. These maps help in optimizing fertilizer application, irrigation planning, crop selection, and soil health improvement practices. The result is improved resource efficiency, higher yield, and sustainable field management with reduced input wastage.
Process Flow
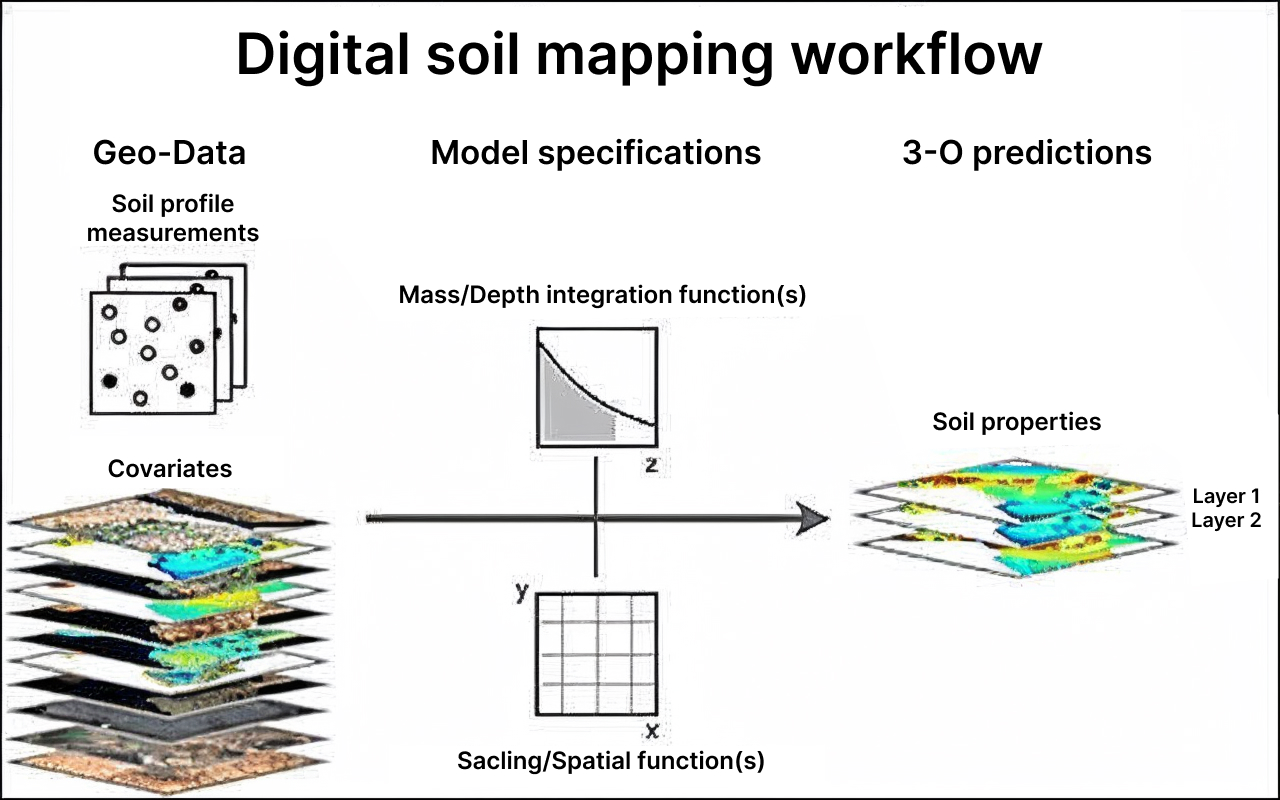
Image source : Workflow of digital soil mapping | Download Scientific Diagram
The digital soil mapping workflow begins with a drone capturing multispectral or hyperspectral imagery, elevation data, and surface reflectance, which act as spatial covariates showing variation in soil moisture, texture, organic matter, and nutrient-related signals. Along with this, a few ground soil samples are collected to provide accurate reference values. These drone layers and soil sample results are then combined in a modeling system that applies depth-integrating functions to interpret soil properties vertically (Z-axis) and spatial scaling functions to map horizontal field variability (X–Y axis). Using machine learning, the system correlates drone-derived data with measured soil values to predict soil characteristics across the entire field. The final output is a 3D soil property map showing nutrient levels, pH, EC, organic carbon, texture, and moisture for different soil depths, enabling precision decisions for fertilization, irrigation, and soil health management.
Reference Image
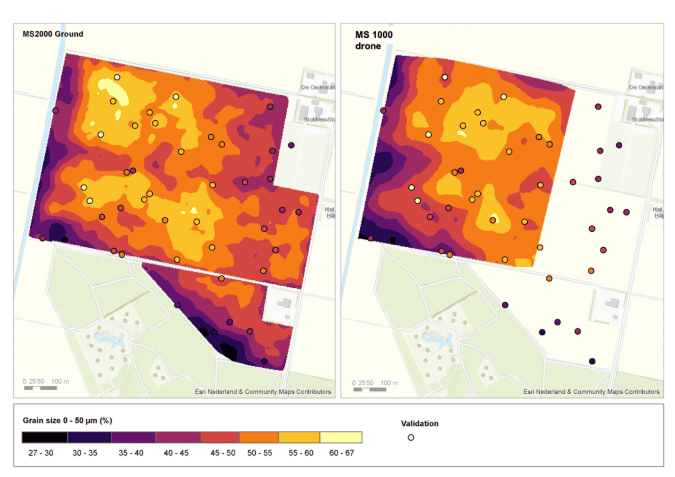
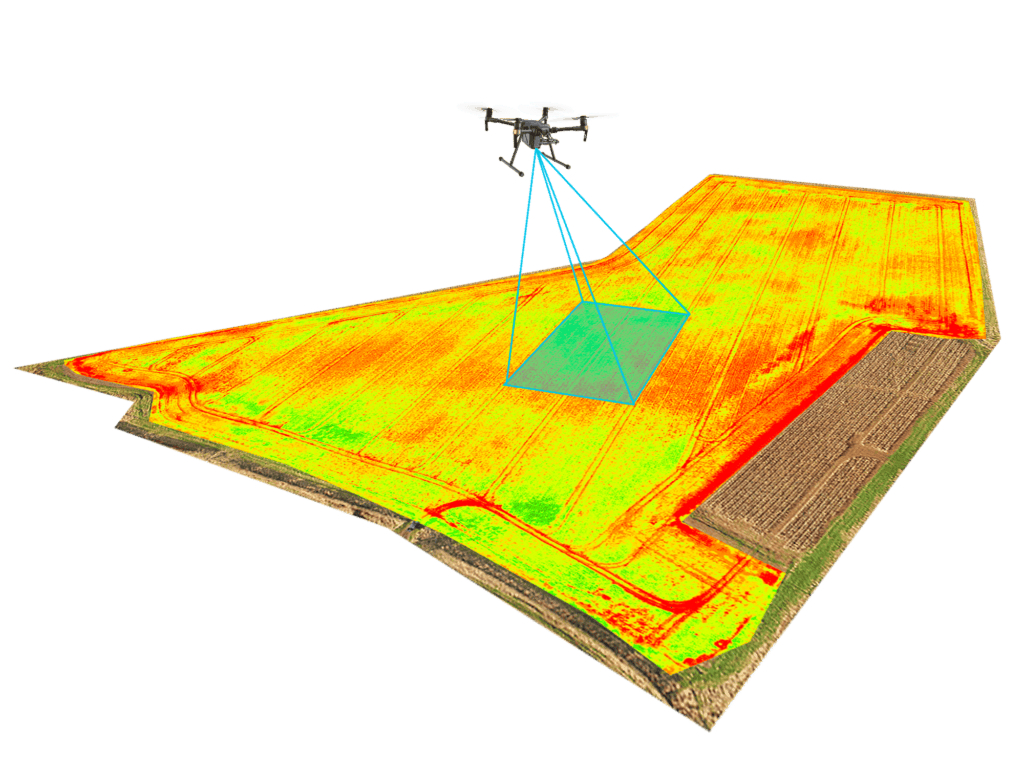
- Process Flow of soil mapping and analysis using drone – Search ImagesDrone for Agriculture
- Drone Use for Various Fields Like Research Analysis, Safety,rescue, Terrain Scanning Technology, Monitoring Stock Image – Image of innovation, agritech: 101333669
- Soil mapping with drones | GIM International
Relevant Outcomes / Deliverables
- Spatial maps of N, P, K, organic carbon, pH, EC, and micronutrient variation across the field
- Identification of sandy, loamy, and clay zones with moisture variability
- Classification of fields into low, medium, and high fertility zones
- Depth-wise soil property analysis for root-zone management
- Prescriptive maps for fertilizer, lime, gypsum, and water application
- Data-driven recommendations for nutrient balance and soil structure
- Year-over-year soil health tracking
- Improved crop rotation and land management planning
Achievable Accuracy
| Parameter | Achievable Accuracy / Units |
|---|---|
| Soil Nutrient Mapping (N, P, K, OC) | 90% accuracy |
| Soil pH & EC Mapping | ±0.5 pH units / ±10% EC error |
| Soil Texture Classification | 92% accuracy |
| Soil Moisture Mapping | ±15% volumetric error |
| 3D Depth-wise Prediction | 85% accuracy |
| Fertility Zonation | 95% accuracy |
| Digital Elevation & Terrain Models | 2–10 cm vertical accuracy |
Key Advantages
- Identifies exact soil nutrient levels and deficiencies
- Enables variable-rate input application
- Supports targeted soil amendments
- Maps moisture zones for efficient irrigation
- Ensures nutrients reach the right depth and location
- Provides depth-wise soil intelligence
- Improves field uniformity through precision interventions
- Assists in crop and variety selection
- Tracks soil health trends year over year
Compatible Drone Platforms
- Dristi
- Dristi Pro
Supported Sensors / Payloads
- Multispectral or hyperspectral sensor
- GNSS module for precise positioning
- Optional ground-truth soil probe integration
Industry Segments Benefited
- Agriculture & Farming
- Agri-Tech & Precision Agriculture
- Land & Environmental Management
- Forestry & Horticulture
- Construction & Civil Engineering
- Research & Academia



