Crop Health Monitoring (Multispectral Sensor)
Overview
Multispectral drones provide wide-ranging applications across agriculture and environmental monitoring. In precision agriculture, they deliver detailed crop health mapping by detecting early signs of disease, pest infestation, nutrient deficiency, and water stress. This enables targeted interventions such as optimized fertilization and irrigation, improving yields while reducing resource wastage.
Process Flow
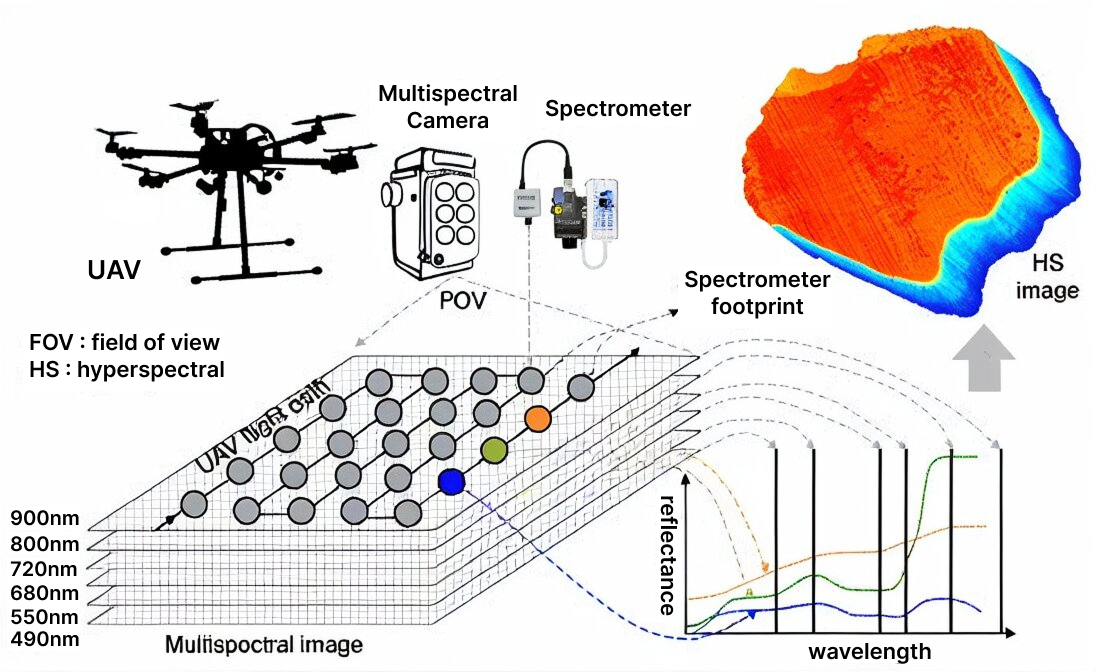
This image represents the working process of our drone equipped with a multispectral camera. As the drone flies over the target field, the multispectral camera captures images at different wavelength bands such as 490 nm, 550 nm, 680 nm, 720 nm, 800 nm, and 900 nm. These images help record the light reflectance from crops and soil in various spectral ranges. At the same time, the spectrometer collects detailed reflectance data from a specific area to maintain radiometric accuracy and ensure reliable calibration. The captured data layers are then combined to generate a image, which provides information on crop health, nutrient levels, and stress conditions. This process enables Drishti drone to deliver accurate, data-driven insights for precision agriculture and field monitoring.
Reference Images
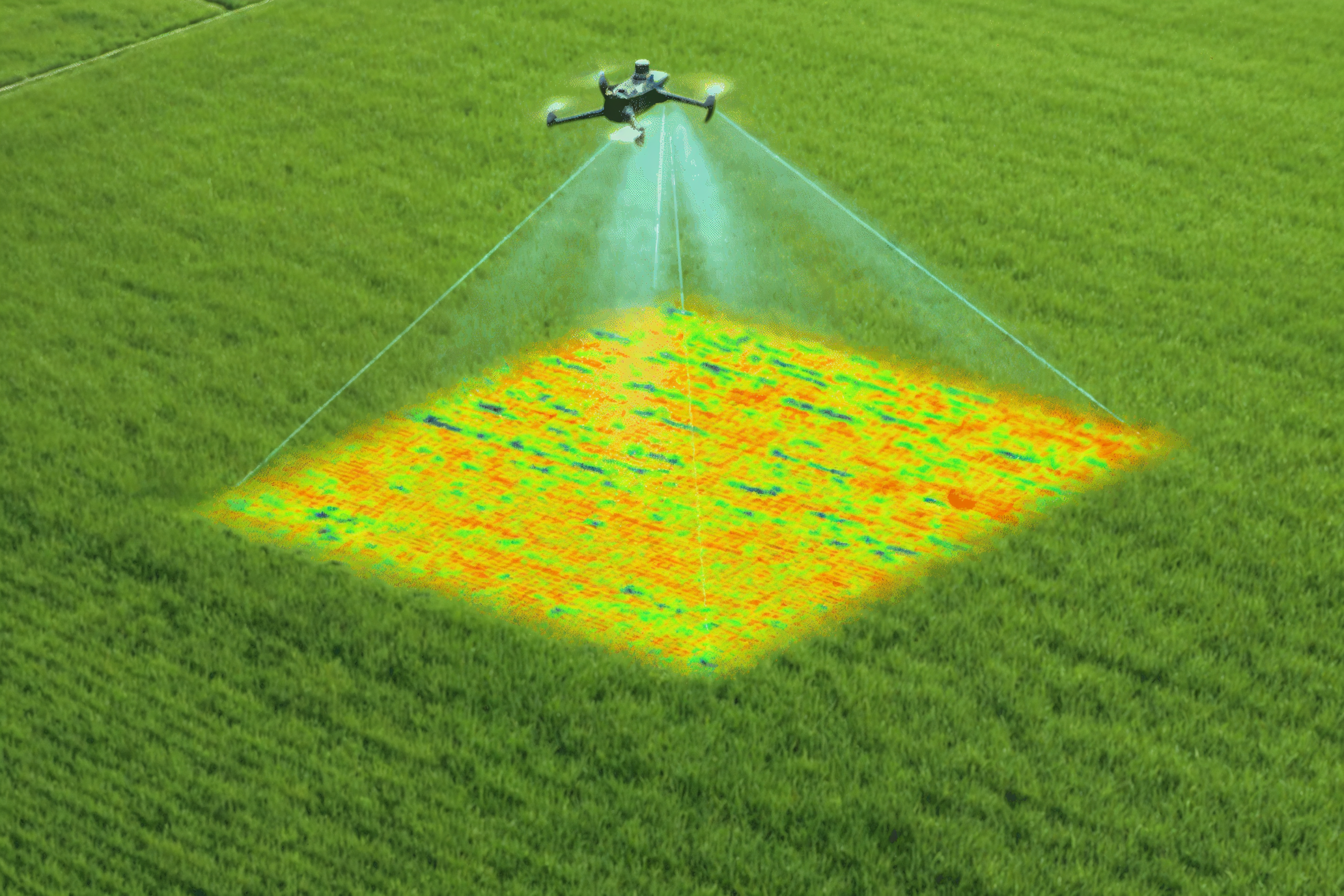
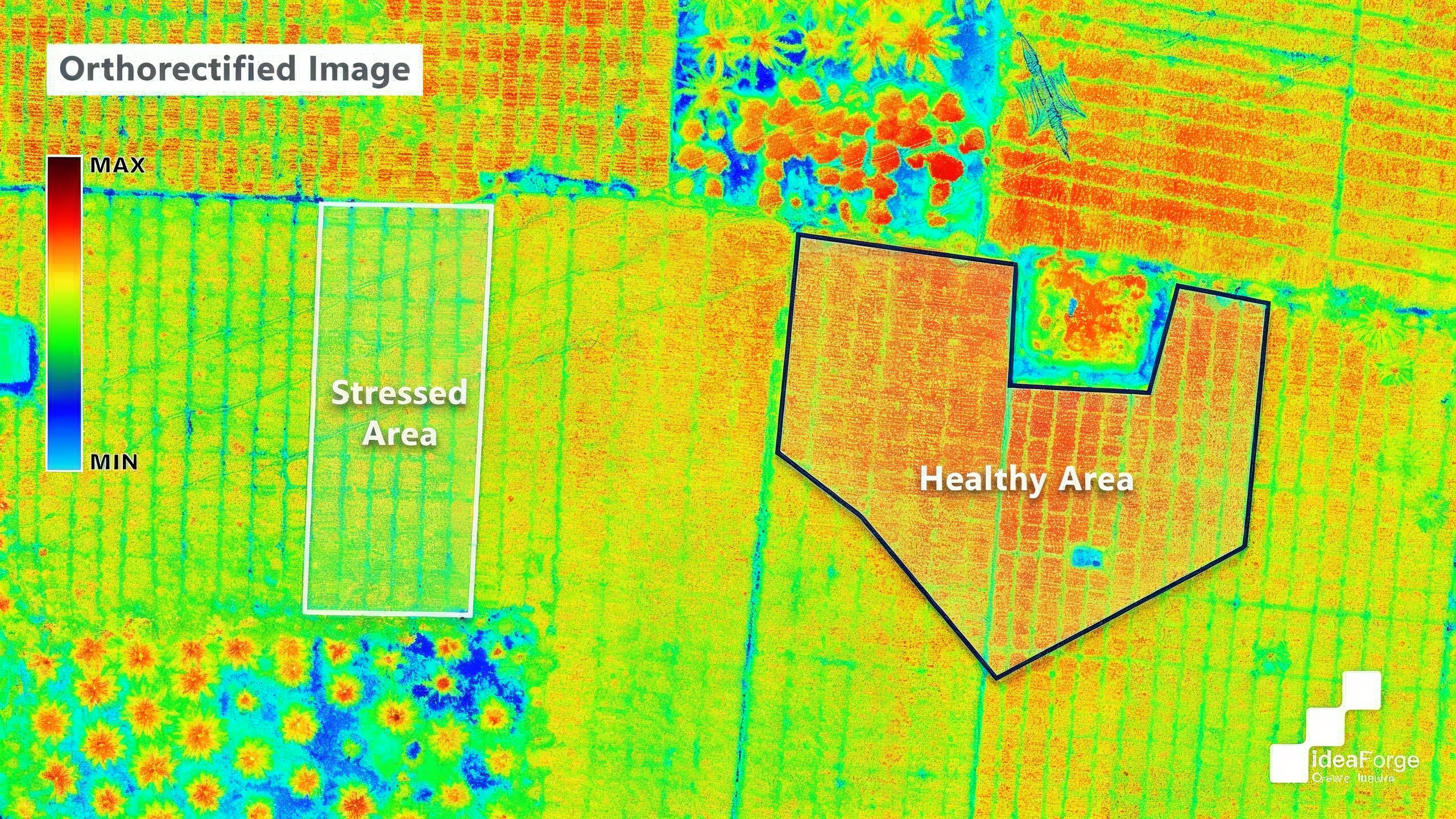
Relevant Outcomes / Deliverables
| Deliverable | Usage |
|---|---|
| Multispectral Imagery & Maps | High-resolution images across RGB, NIR, and Red-edge bands |
| Vegetation Index Maps (NDVI, NDRE) | Quantitative assessment of crop health and stress |
| Orthomosaic Maps | Georeferenced stitched maps for spatial analysis |
| Crop Health Reports | Identification of disease zones, nutrient deficiency, and stress |
| Soil & Moisture Analysis | Evaluation of soil variability and water distribution |
| 3D Terrain & Canopy Models | Elevation, canopy height, and biomass estimation |
Achievable Accuracy
| Parameter | Typical Accuracy | Depends On |
|---|---|---|
| Radiometric Accuracy | ±3–5% | Calibration using reflectance panels |
| Spectral Band Accuracy | 1–2 pixels | Image resolution and sensor alignment |
| Sensor Accuracy | ±2–3% | Environmental and lighting conditions |
Key Advantages
- Detects crop stress, disease, and nutrient deficiencies before visible symptoms
- Enables precise fertilizer, pesticide, and irrigation application
- Covers large areas faster than manual field scouting
- Generates reliable NDVI/NDRE for plant health monitoring
- Supports forest, wetland, and ecosystem conservation
- Provides rapid assessment for disaster recovery and damage analysis
- Enables frequent monitoring with high spatial detail
Compatible Drone Platforms
- Drishti
Supported Sensors / Payloads
- Multispectral sensors (e.g., MicaSense, Sentera)
- GNSS + IMU for precise geotagging
- Cloud-based analytics platform for processing and reporting
Industry Segments Benefited
Agriculture & Precision Farming, Forestry & Ecosystem Management, Environmental Monitoring, Mining & Geology, Coastal & Marine Studies, Urban Planning & Land Management, Defense & Surveillance.
References
- Evaluation of UAV-Based RGB and Multispectral Vegetation Indices for Precision Agriculture in Palm Tree Cultivation
- A review of the application of UAV multispectral remote sensing technology in precision agriculture – ScienceDirect
- Full article: Monitoring of crop fields using multispectral and thermal imagery from UAV
- An Object-Based Image Analysis Workflow for Monitoring Shallow-Water Aquatic Vegetation in Multispectral Drone Imagery
- Weed mapping in multispectral drone imagery using lightweight vision transformers – ScienceDirect



